import graphviz
# This output is generated from the model
# as you can see, there are several decisions
# to make, and the hyrarchy can be compiled like a tree
graphviz.Source.from_file('cache/iristree.dot')Machine Learning - Supervised Learning
first we need to import pandas and load the data with pd.read_csv(file)
import pandas as pd
iris = pd.read_csv('datasets/iris/Iris.csv')this is the overview of the data
iris| Id | SepalLengthCm | SepalWidthCm | PetalLengthCm | PetalWidthCm | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 1 | 2 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 2 | 3 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 3 | 4 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 4 | 5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 145 | 146 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 146 | 147 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 1.9 | Iris-virginica |
| 147 | 148 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.0 | Iris-virginica |
| 148 | 149 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 5.4 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 149 | 150 | 5.9 | 3.0 | 5.1 | 1.8 | Iris-virginica |
150 rows × 6 columns
if we wan to check detail about the data, use data.info()
iris.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Id 150 non-null int64
1 SepalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
2 SepalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
3 PetalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
4 PetalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
5 Species 150 non-null object
dtypes: float64(4), int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 7.2+ KBthe Id is not needed in this case, therefore we can just drop it
# stropping unneeded data
iris.drop('Id', axis=1, inplace=True)| Id | SepalLengthCm | SepalWidthCm | PetalLengthCm | PetalWidthCm | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 1 | 2 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 2 | 3 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 3 | 4 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 4 | 5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
now, we separate the data label from its features, and save it to X and y, we need also to separate the data to train and split
X = iris[['SepalLengthCm', 'SepalWidthCm', 'PetalLengthCm', 'PetalWidthCm']]
y = iris['Species']
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=123)we prepare the model by calling it from sklearn.tree
from sklearn import tree
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()# With defined train test split
clf = clf.fit(X_train, y_train)conclusion on cross_val_score
cross_val_score is for validating the quality of data set, it’s consider good if it’s more than 0.85
# with cross validation
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5)scoresarray([0.96666667, 0.96666667, 0.9 , 0.96666667, 1. ])# model evaluation
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print(y_pred)
print(y_test)
acc_score = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_test), 3)
print('accuracy', acc_score)['Iris-virginica' 'Iris-virginica' 'Iris-virginica' 'Iris-versicolor'
'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-virginica' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-setosa'
'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-virginica' 'Iris-setosa'
'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-virginica' 'Iris-virginica']
72 Iris-versicolor
112 Iris-virginica
132 Iris-virginica
88 Iris-versicolor
37 Iris-setosa
138 Iris-virginica
87 Iris-versicolor
42 Iris-setosa
8 Iris-setosa
90 Iris-versicolor
141 Iris-virginica
33 Iris-setosa
59 Iris-versicolor
116 Iris-virginica
135 Iris-virginica
Name: Species, dtype: object
accuracy 0.933print(clf.predict([[6.2, 3.4, 5.4, 2.3]])[0])from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
export_graphviz(
clf,
out_file = 'cache/iristree.dot',
feature_names = ['SepalLengthCm', 'SepalWidthCm', 'PetalLengthCm', 'PetalWidthCm'],
class_names = ['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica' ],
rounded= True,
filled =True)Regression
Linear Regression
import numpy as np
# make dummy data of rooms
bedrooms = np.array([1,1,2,2,3,4,4,5,5,5])
# make dummy price data in dolar
house_price = np.array([15000, 18000, 27000, 34000, 50000, 68000, 65000, 81000,85000, 90000])# visualize in scatterplot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.scatter(bedrooms, house_price)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# train the model with LinearRegression.fit()
bedrooms = bedrooms.reshape(-1, 1)
linreg = LinearRegression()
linreg.fit(bedrooms, house_price)LinearRegression()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LinearRegression()
# plotting the corelation between number of rooms and house_prices
plt.scatter(bedrooms, house_price)
plt.plot(bedrooms, linreg.predict(bedrooms))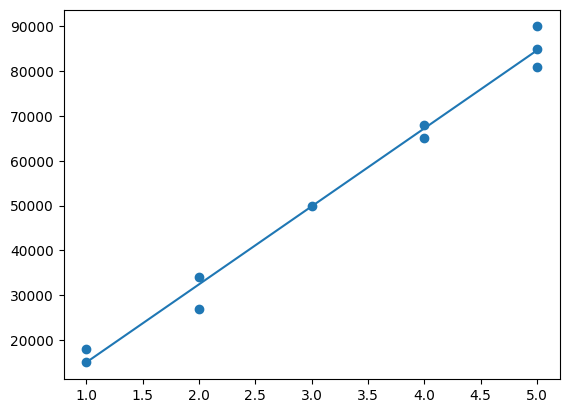
Logistic Regression
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('datasets/socmedAds/Social_Network_Ads.csv')
df| User ID | Gender | Age | EstimatedSalary | Purchased | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15624510 | Male | 19 | 19000 | 0 |
| 1 | 15810944 | Male | 35 | 20000 | 0 |
| 2 | 15668575 | Female | 26 | 43000 | 0 |
| 3 | 15603246 | Female | 27 | 57000 | 0 |
| 4 | 15804002 | Male | 19 | 76000 | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 395 | 15691863 | Female | 46 | 41000 | 1 |
| 396 | 15706071 | Male | 51 | 23000 | 1 |
| 397 | 15654296 | Female | 50 | 20000 | 1 |
| 398 | 15755018 | Male | 36 | 33000 | 0 |
| 399 | 15594041 | Female | 49 | 36000 | 1 |
400 rows × 5 columns
df.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 400 entries, 0 to 399
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 User ID 400 non-null int64
1 Gender 400 non-null object
2 Age 400 non-null int64
3 EstimatedSalary 400 non-null int64
4 Purchased 400 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(4), object(1)
memory usage: 15.8+ KBdata = df.drop(columns=['User ID'])
data = pd.get_dummies(data)
data| Age | EstimatedSalary | Purchased | Gender_Female | Gender_Male | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 19 | 19000 | 0 | False | True |
| 1 | 35 | 20000 | 0 | False | True |
| 2 | 26 | 43000 | 0 | True | False |
| 3 | 27 | 57000 | 0 | True | False |
| 4 | 19 | 76000 | 0 | False | True |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 395 | 46 | 41000 | 1 | True | False |
| 396 | 51 | 23000 | 1 | False | True |
| 397 | 50 | 20000 | 1 | True | False |
| 398 | 36 | 33000 | 0 | False | True |
| 399 | 49 | 36000 | 1 | True | False |
400 rows × 5 columns
X = data[['Age', 'EstimatedSalary', 'Gender_Female', 'Gender_Male']]
y = data['Purchased']# data normalization
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
# calculating the mean and standard deviation of every attribute column
# to be used on every transform function
scaler.fit(X)
scaled_data = scaler.transform(X)
scaled_data = pd.DataFrame(scaled_data, columns=X.columns)
scaled_data| Age | EstimatedSalary | Gender_Female | Gender_Male | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.781797 | -1.490046 | -1.020204 | 1.020204 |
| 1 | -0.253587 | -1.460681 | -1.020204 | 1.020204 |
| 2 | -1.113206 | -0.785290 | 0.980196 | -0.980196 |
| 3 | -1.017692 | -0.374182 | 0.980196 | -0.980196 |
| 4 | -1.781797 | 0.183751 | -1.020204 | 1.020204 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 395 | 0.797057 | -0.844019 | 0.980196 | -0.980196 |
| 396 | 1.274623 | -1.372587 | -1.020204 | 1.020204 |
| 397 | 1.179110 | -1.460681 | 0.980196 | -0.980196 |
| 398 | -0.158074 | -1.078938 | -1.020204 | 1.020204 |
| 399 | 1.083596 | -0.990844 | 0.980196 | -0.980196 |
400 rows × 4 columns
# validation with cross validation
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn import linear_model
model = linear_model.LogisticRegression()
scores = cross_val_score(model, scaled_data, y, cv=5)scoresarray([0.7 , 0.95 , 0.9375, 0.8125, 0.7 ])from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(scaled_data, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1)model.fit(X_train, y_train)LogisticRegression()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression()
# examine model accuracy
model.score(X_test, y_test)0.825